Saffron
Saffron: A Unique Plant with Exceptional Color and Aroma
Saffron, known for its distinctive color and fragrance, is used as a spice and seasoning in cooking. This plant also has medicinal properties and is recognized as one of the most expensive and valuable plants in the world. Due to its rarity, saffron is often referred to as “Red Gold.” Understanding the different types of saffron, their distinctions, and the methods of saffron cultivation is of great importance.
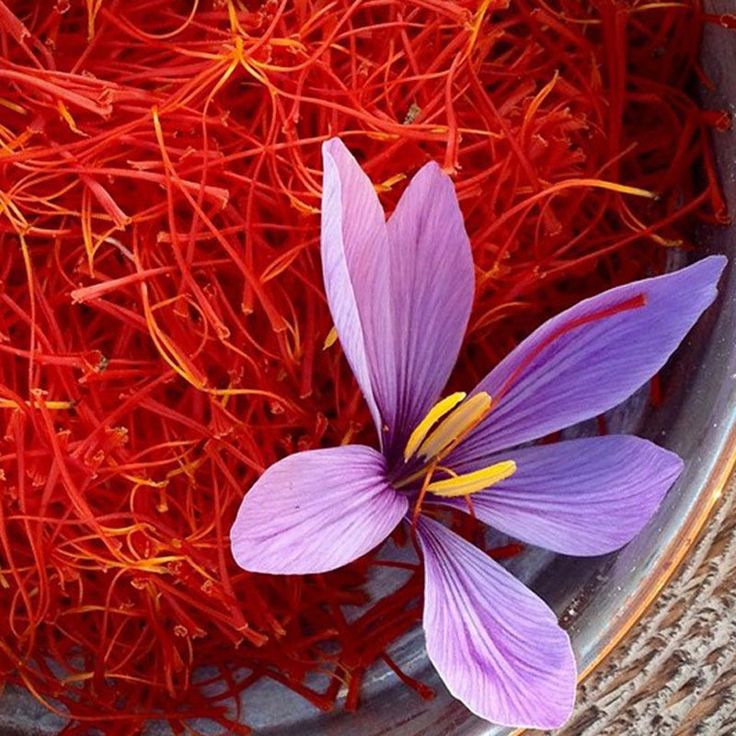
Saffron is a plant that grows to a height of about 30 centimeters, with long green leaves resembling chives. The underground stem of saffron consists of two fleshy bulbs, covered with thin brown membranes. Saffron flowers have long, orderly tubes in a purple hue, ending in sepals and three petals. Different varieties of saffron possess varying qualities.

Types of Saffron and Their Differences
What you will read on this page
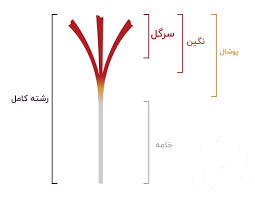
ToggleEach saffron thread consists of two main parts, which are very important in distinguishing different types of saffron: the first part is the stigma (the red part of saffron), and the second part is the style (the white part of saffron). Below, we will introduce the different types of saffron flowers in Iran and their differences:
Daughter-pitch or bunch saffron

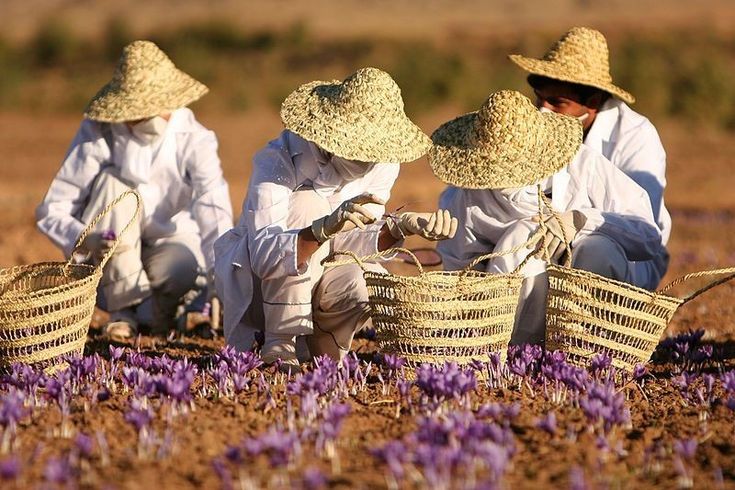
In ancient times, hardworking women and girls played an important role in saffron processing, from planting and harvesting to packaging. For this reason, this type of saffron became known as “Daughter-pitch.” Even today, in many parts of the world, saffron is still packaged using traditional and manual methods, with this task remaining the responsibility of women and girls.
Daughter-pitch saffron, or bunch saffron, consists of threads that contain both the yellow and red parts of saffron. The yellow part makes up about 30% and the red part constitutes 70% of its weight. This type of saffron is arranged in two different ways: in the one-way model, the stigmas and styles are placed separately on top of each other, while in the two-way model, the stigmas are positioned on both sides and the styles are in the middle
Saffron Pushal

One type of saffron is Pushal saffron. This type of saffron is produced during the harvesting process in a way that the stigmas are separated from the lower part of the red section, the style. The stigmas usually have 1 to 3 millimeters of style and the ends of the three branches are marked with yellow or white. This characteristic has made it famous as “Pushal saffron.”
Pushal saffron is classified into two types:
- Regular Pushal: Includes curled stigmas with more style.
- Premium Pushal: Has straight, thick stigmas with less style.
Sargol saffron

Sargol saffron is known for the separation of the cream from the stigma. Only the upper, red part of the saffron threads, known as the stigma, is used to produce this type of saffron. One of the most important features of Sargol saffron is the uniformity of its threads and its exceptional coloring power. Due to its high quality and intense coloring strength, this type of saffron is considered one of the most popular varieties.
This type of saffron is obtained by cleaning and sifting the Pushal and Daughterpeych saffron. In this process, some threads may break or turn into powder, but the final quality remains high.
Negin saffron

Negin saffron is one of the highest quality and most sought-after types of saffron, with many customers in domestic and regional markets. This saffron holds a special place among saffron varieties due to its exceptional coloring, beautiful appearance, and extraordinary fragrance. In Negin saffron, the three red stigmas are smooth, connected, and unbroken, whereas in Sargol saffron, the stigmas are usually broken. This feature gives Negin saffron superiority in terms of price and appearance compared to Sargol saffron.
Negin saffron is divided into three categories: Semi-Negin, Super-Negin, and Pressed-Negin:
- Super-Negin: Saffron with a length longer than 2.5 cm.
- Semi-Negin: Saffron similar to Super-Negin but with a yellow part at the end of the stigma.
- Pressed-Negin: Saffron that is dried using an ironing method to ensure the threads are perfectly smooth, uniform, and unbroken.
White saffron

In the saffron separation process, after separating the red saffron stigmas (known as “Sargol”) from the saffron bundle, a white part of the saffron thread remains. This part, known in Iran as white saffron, konj, or saffron cream, is used as one of the components of saffron. Contrary to the common belief that saffron roots have a stronger fragrance, the red part of saffron is also rich in valuable compounds.
Konj saffron or saffron cream, due to its natural properties, can be beneficial for improving certain issues such as depression, skin rejuvenation and freshness, liver and heart function, and even eliminating bad breath.
Saffron Narme or Broken Saffron

Broken Saffron is a type of saffron that, during the process of separating and drying the saffron stigmas from the flower, becomes broken and fragmented due to handling and pressure. Despite its broken appearance, this type of saffron retains the same fragrance, aroma, and color strength as Saffron Sergol (flower threads) or Negin saffron.
One of the reasons for the popularity of Saffron Narma is its high quality combined with its more affordable price compared to other types of saffron. Although it appears broken, it does not differ in terms of color strength and quality from premium saffron varieties.
Saffron cultivation methods
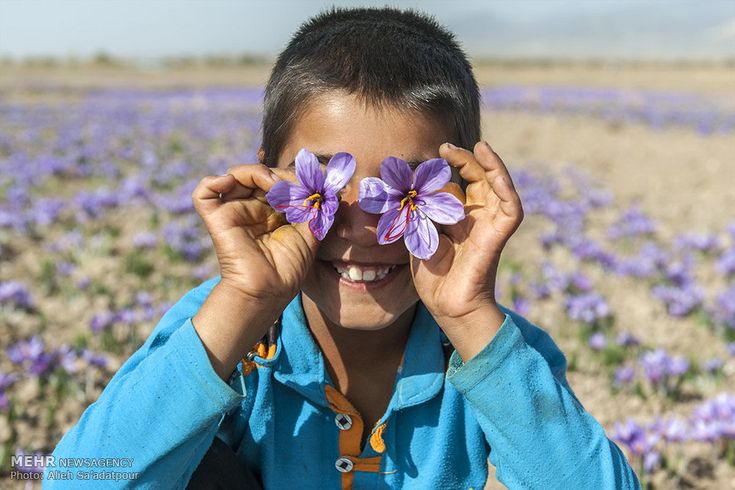

Saffron is one of the plants that requires very little water for growth. Its growing season coincides with the autumn and winter rains, which significantly reduces its water consumption. Unlike in the past when saffron cultivation was limited to Khorasan Province, today it can be grown in areas such as Isfahan, Tabriz, and parts of Mazandaran.
Methods of saffron cultivation:
- Traditional (Soil) Cultivation: This old and widely used method is one of the most cost-effective ways to cultivate saffron.
- Greenhouse Cultivation: The most advanced method of saffron cultivation, which offers higher productivity due to controlled conditions.
- Home Cultivation: People who wish to grow saffron in small areas such as their homes can use this method
Quality Control Guidelines for Saffron

Red gold, or saffron, due to its high economic value and expensive price, has always been a target for fraudsters who offer counterfeit products. Various methods exist for producing fake saffron; for example, some individuals coat the saffron stigma with artificial colors and sell it as genuine saffron. Materials such as shredded paper, safflower plants, or even coconut fibers are also used to mimic the appearance of saffron.
To combat fraud in saffron sales, quality and purity control are essential. Producers need to obtain certification from reputable laboratories to confirm the authenticity of their saffron. This certification is particularly important in the saffron export process. The quality of saffron is also determined by the method of planting and harvesting
Types of Saffron Quality (Varieties of Saffron Quality)
Saffron quality is an indicator of its purity and excellence. This measure is determined in specialized laboratories based on various factors. The quality of saffron varies depending on characteristics such as taste, aroma, coloring strength, thread length, foreign materials content, and moisture level. Below, we examine each of these factors:
Taste of Saffron: The compound picocrocin in saffron gives it a bitter taste. The standard amount of this substance should range from 70 to 150.
Aroma of Saffron: The aroma is one of the key factors in determining the quality and depends on the presence of the compound safranal. The amount of this substance should be between 20 to 50 units.
Coloring Strength and Quality of Saffron: The compound crocin is responsible for saffron’s coloring and is one of the primary factors in determining its quality. The standard amount of this compound should be between 140 to 300 units, depending on the type of saffron.
Length of Saffron Threads: In premium saffron types like “Sargol,” the length of the threads is crucial. The standard length typically ranges from 10 to 30 millimeters.
Foreign Materials: The presence of foreign materials in saffron is examined in laboratories. The standard amount of foreign materials should be less than 2% by weight.
Moisture Content: The moisture level in saffron also impacts its quality. The standard moisture content should be less than 10% by weight.
The best types of export-quality saffron in Iran.

The most essential and important types of Iranian saffron for export are Negin saffron, Super Negin saffron, and Sargol saffron. Each market demands a specific quality and type of saffron. For example, Negin saffron is the highest quality and is not suitable for all markets and countries.
Methods of Exporting Saffron
There are various methods for exporting saffron. Here are six important stages for saffron export, followed by additional key points:
1. Determining the Saffron Export Strategy
Saffron is exported in two ways: bulk and packaged.
- Bulk Saffron: Typically in half or one-kilogram quantities. Unfortunately, bulk saffron is often repackaged by foreign brands and re-imported into Iran, which harms Iranian saffron exports.
- Packaged Saffron: Exported in packages of under 30 grams. This type of export provides opportunities for branding and adding value through appropriate packaging.
2. International Marketing and Understanding the Global Market
Accessing international customers through connections with trade attachés, traders, and chambers of commerce, as well as participating in international trade shows, is essential. The country you choose to export to is crucial, as each country has its own demand for saffron. For example:
- Turkey: Saffron is mainly purchased by tourists.
- Iraq: Saffron is used for fragrance and color.
- European Countries: Saffron is primarily used for medicinal purposes. Proper marketing and understanding the market of the destination country are fundamental.
3. Obtaining Saffron and Proper Packaging
You can either cultivate saffron yourself or source it from farmers who produce high-quality saffron. Regardless, the saffron you choose for export must be of the highest quality. Packaging plays a key role in attracting customers and competing in international markets. For example:
- In Saudi Arabia: Crystal containers are used.
- In European markets: Metal containers are preferred to ensure the container is reusable after the saffron is finished. Effective advertising and appealing packaging are the most important factors for success.
4. Obtaining Necessary Export Permits
The necessary permits for saffron export include:
- Export permit
- Health permit
- Business card
- Tax declaration
- Product registration at the Iranian customs
- Standard certification Once the customs verifies the documents and tariff details, the saffron is cleared for export, and the relevant documents are sent along with the shipment.
5. Pricing of Export Saffron
To determine the correct price for your product, use a pricing commission to find an appropriate price. For saffron pricing, ensure you achieve a good profit margin without incurring losses. Consider payment methods, sales terms, packaging costs, insurance, transport fees, and the value of the saffron in the pricing process.
If you’re exporting saffron for the first time, it’s essential to consult with those experienced in export companies or business consulting firms to benefit from their knowledge.
6. Export Insurance for Saffron
Insurance is a crucial aspect of export. Be sure to use export insurance to protect against any unforeseen events that may lead to losses. Insurance is the responsibility of the seller.
Key Points in Saffron Export
Types of Iranian Export Saffron: Iranian export saffron includes Negin, Super Negin, and Sargol saffron. Each international market has specific preferences. For instance, Negin saffron is of the highest quality but may not be suitable for all markets.
Six Main Stages of Saffron Export:
- Export Strategy: Decide whether to export saffron in bulk or packaging.
- International Marketing: Understanding the market and target audience.
- Saffron Procurement and Packaging: Selecting high-quality saffron and using appropriate packaging for each market.
- Obtaining Permits: Ensure all necessary documentation and permits are in place.
- Pricing: Set competitive pricing while considering all associated costs.
- Insurance: Protect your shipment with appropriate insurance.
Conclusion
Novin Atra: As a supplier of authentic Iranian saffron, Novin Atra ensures the highest quality saffron, competitive pricing, and optimal packaging for international markets. Trust Novin Atra to make your saffron export journey successful and sustainable

